KAVM
http://kavm.blogspot.com/
शुक्रवार, 22 मार्च 2019
शुक्रवार, 15 मार्च 2019
https://clicksfly.com/payout-rates
https://clicksfly.com/payout-rates
Minimum Payout: $3
Payment Frequency: Weekly, Monthly
Payment Methods: Bitcoin, PayPal, Payoneer, Paytm [India], Bank Transfer [India], Payeer, TEZ, UPI
Note: This Rate Are Our Approx CPM Rate. We Change Our CPM rate Daily
Our Minimum Rate For All Country Is 3$ CPM!!
Payment Frequency: Weekly, Monthly
Payment Methods: Bitcoin, PayPal, Payoneer, Paytm [India], Bank Transfer [India], Payeer, TEZ, UPI
Note: This Rate Are Our Approx CPM Rate. We Change Our CPM rate Daily
Our Minimum Rate For All Country Is 3$ CPM!!
We count 5+ views per IP within 24 hours By which you will be benefited more.
| Package Description / Country | Earnings per 1000 Views | |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | Mobile / Tablet | |
| France | $15.00 | $15.00 |
| Saudi Arabia | $13.00 | $13.00 |
| United States | $12.00 | $12.00 |
| Netherlands | $12.00 | $12.00 |
| Australia | $11.00 | $11.00 |
| United Kingdom | $10.00 | $10.00 |
| New Zealand | $10.00 | $10.00 |
| Ireland | $8.00 | $8.00 |
| Belgium | $8.00 | $8.00 |
| Canada | $6.20 | $6.20 |
| Singapore | $6.20 | $6.20 |
| Germany | $6.00 | $6.00 |
| Hong Kong | $6.00 | $6.00 |
| Norway | $6.00 | $6.00 |
| Denmark | $5.80 | $5.80 |
| Sweden | $5.60 | $5.60 |
| Switzerland | $5.20 | $5.20 |
| Thailand | $4.20 | $4.20 |
| Finland | $4.00 | $4.00 |
| Kuwait | $4.00 | $4.00 |
| Philippines | $4.00 | $4.00 |
| India | $3.80 | $3.80 |
| Worldwide Deal(All Countries) | $3.50 | $3.50 |
| South Africa | $3.50 | $3.50 |
| Brazil | $3.50 | $3.50 |
| Portugal | $3.00 | $3.00 |
| Venezuela | $2.50 | $2.50 |
| Russian Federation | $2.50 | $2.50 |
| Mexico | $2.00 | $2.00 |
| Morocco | $2.00 | $2.00 |
| Indonesia | $2.00 | $2.00 |
| Nigeria | $2.00 | $2.00 |
Fake/Bot/Pop Up/Adult Traffic Are Not Allowed
We Use Google Served Ads Adsense As Your traffic Also Follow Google Ads Policy.
We Use Google Served Ads Adsense As Your traffic Also Follow Google Ads Policy.
मंगलवार, 26 जनवरी 2016
Server in Level of RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
This article is about the data storage technology. For other uses, see Raid (disambiguation).
RAID (originally redundant array of inexpensive disks, now commonly redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into a single logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.[1]Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as RAID levels, depending on the required level of redundancy and performance. The different schemas, or data distribution layouts, are named by the word RAID followed by a number, for example RAID 0 or RAID 1. Each schema, or a RAID level, provides a different balance among the key goals: reliability, availability, performance, and capacity. RAID levels greater than RAID 0 provide protection against unrecoverable sector read errors, as well as against failures of whole physical drives.
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
by Meghraj
On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAIDs.
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0)
In all the diagrams mentioned below:
- A, B, C, D, E and F – represents blocks
- p1, p2, and p3 – represents parity
RAID LEVEL 0

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0.
- Minimum 2 disks.
- Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ).
- No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ).
- Don’t use this for any critical system.
RAID LEVEL 1

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.
- Minimum 2 disks.
- Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
- Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
RAID LEVEL 5
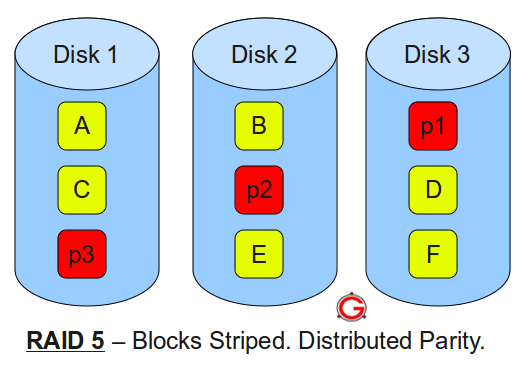
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5.
- Minimum 3 disks.
- Good performance ( as blocks are striped ).
- Good redundancy ( distributed parity ).
- Best cost effective option providing both performance and redundancy. Use this for DB that is
- heavily read oriented. Write operations will be slow.
RAID LEVEL 10
Standard levels
Main article: Standard RAID levels
- RAID 0
- RAID 0 consists of striping, without mirroring or parity. The capacity of a RAID 0 volume is the sum of the capacities of the disks in the set, the same as with a spanned volume. There is no added redundancy for handling disk failures, just as with a spanned volume. Thus, failure of one disk causes the loss of the entire RAID 0 volume, with reduced possibilities of data recovery when compared to a broken spanned volume. Striping distributes the contents of files roughly equally among all disks in the set, which makes concurrent read or write operations on the multiple disks almost inevitable and results in performance improvements. The concurrent operations make the throughput of most read and write operations equal to the throughput of one disk multiplied by the number of disks. Increased throughput is the big benefit of RAID 0 versus spanned volume.
- RAID 1
- RAID 1 consists of data mirroring, without parity or striping. Data is written identically to two (or more) drives, thereby producing a "mirrored set" of drives. Thus, any read request can be serviced by any drive in the set. If a request is broadcast to every drive in the set, it can be serviced by the drive that accesses the data first (depending on its seek time and rotational latency), improving performance. Sustained read throughput, if the controller or software is optimized for it, approaches the sum of throughputs of every drive in the set, just as for RAID 0. Actual read throughput of most RAID 1 implementations is slower than the fastest drive. Write throughput is always slower because every drive must be updated, and the slowest drive limits the write performance. The array continues to operate as long as at least one drive is functioning.
- RAID 2
- RAID 2 consists of bit-level striping with dedicated Hamming-code parity. All disk spindle rotation is synchronized and data is striped such that each sequential bit is on a different drive. Hamming-code parity is calculated across corresponding bits and stored on at least one parity drive.This level is of historical significance only; although it was used on some early machines (for example, the Thinking Machines CM-2), as of 2014 it is not used by any of the commercially available systems.
- RAID 3
- RAID 3 consists of byte-level striping with dedicated parity. All disk spindle rotation is synchronized and data is striped such that each sequential byte is on a different drive. Parity is calculated across corresponding bytes and stored on a dedicated parity drive. Although implementations exist, RAID 3 is not commonly used in practice.
- RAID 4
- RAID 4 consists of block-level striping with dedicated parity. This level was previously used by NetApp, but has now been largely replaced by a proprietary implementation of RAID 4 with two parity disks, called RAID-DP. The main advantage of RAID 4 over RAID 2 and 3 is I/O parallelism: in RAID 2 and 3, a single read/write I/O operation requires reading the whole group of data drives, while in RAID 4 one I/O read/write operation does not have to spread across all data drives. As a result, more I/O operations can be executed in parallel, improving the performance of small transfers.
- RAID 5
- RAID 5 consists of block-level striping with distributed parity. Unlike RAID 4, parity information is distributed among the drives, requiring all drives but one to be present to operate. Upon failure of a single drive, subsequent reads can be calculated from the distributed parity such that no data is lost. RAID 5 requires at least three disks. RAID 5 is seriously affected by the general trends regarding array rebuild time and the chance of drive failure during rebuild. Rebuilding an array requires reading all data from all disks, opening a chance for a second drive failure and the loss of the entire array. In August 2012, Dell posted an advisory against the use of RAID 5 in any configuration on Dell EqualLogic arrays and RAID 50 with "Class 2 7200 RPM drives of 1 TB and higher capacity" for business-critical data.
- RAID 6
- RAID 6 consists of block-level striping with double distributed parity. Double parity provides fault tolerance up to two failed drives. This makes larger RAID groups more practical, especially for high-availability systems, as large-capacity drives take longer to restore. RAID 6 requires a minimum of four disks. As with RAID 5, a single drive failure results in reduced performance of the entire array until the failed drive has been replaced. With a RAID 6 array, using drives from multiple sources and manufacturers, it is possible to mitigate most of the problems associated with RAID 5. The larger the drive capacities and the larger the array size, the more important it becomes to choose RAID 6 instead of RAID 5. RAID 10 also minimizes these problems.
RAID 10 (Striping + Mirroring):
RAID 10 combines the mirroring of RAID 1 with the striping of RAID 0. Or in other words, it combines the redundancy of RAID 1 with the increased performance of RAID 0. It is best suitable for environments where both high performance and security is required.

Minimum number of disks: 4See more details on our dedicated server hardware.
Pros: Very high performance. Fault tolerance.
Cons: Lower usable capacity/High cost. Limited scalability
Ideal use: Highly utilized database servers/ servers performing a lot of write operations.
What is important to add is that even though some RAID levels provide data redundancy, it is never to be used as backup of your critical files. RAID protects you against hardware failure, but it does not protect you against errors, file corruption or malicious activity. Always store a complete and recoverable copy of your critical data on a separate hard drive (contact us for back up solutions). If you’re still not sure on which RAID is best for you and your application, send a message to our technical team and they will be happy to assist you with choosing the right solution.
रविवार, 17 जनवरी 2016
Railway Recruitment 2016, 18252 Station Master Clerk Posts- Result24
CENTRALISED EMPLOYMENT
NOTICE CEN.No.03/2015
NON TECHNICAL POPULAR CATEGORIES (GRADUATE)
| Date of publication | 26.12.2015 |
| Date & Time of Closing | 25.01.2016 up to 23.59 Hrs |
| Last Date for Reprint of Application | 25.01.2016 up to 23.59 Hrs |
| Tentative Dates / Slot of Common Computer Based Test / Examination | March - May, 2016 |
| Online Fee payment | 26.12.2015 to 25.01.2016 |
| Offline Fee payment (through SBI/Post office challan) | 28.12.2015 to 22.01.2016 |
Indian Railway Recruitment 2016, Vacancies details:
Total No. of Posts: 18252
Name of Posts:
| Name of Posts | No. Posts | Recruitment Board Name |
| Commercial Apprentice | 703 | Ahmedabad, Ajmer |
| Traffic Apprentice | 1645 | Allahabad, Banglore |
| Enquiry-Cum-Reservation-Clerk | 127 | Bhopal, Bhubaneswar |
| Goods Guard | 7591 | Chennai, Gorakhpur |
| Junior Accounts Assistant-Cum-Typist | 1205 | Guwahati, Jammu-Srinagar |
| Senior Clerk-Cum-Typist | 869 | Kolkata, Malda, Mumbai |
| Assistant Station Master | 5942 | Muzafferpur, Patna |
| Traffic Asst | 166 | Ranchi, Secunderabad |
| Senior Time Keeper | 04 | Siliguri, Thiruvanthapuram |
Eligibility Criteria: Candidates can fill online RRB Recruitment 2016 application as per
below
eligible criteria.
below
eligible criteria.
Age Limit: Age should be between 18 to 32 years as on date 01/01/2016. The upper age
limit is relaxable as under subject to submission of requisite certificates by 5 years for SC/ST,
3 years for OBC Candidates. For Ex-serviceman, up to the extent of service rendered in
Defence plus 3 years, 5 years for candidates who have ordinarily been domiciled in the state
of Jammu & Kashmir.
limit is relaxable as under subject to submission of requisite certificates by 5 years for SC/ST,
3 years for OBC Candidates. For Ex-serviceman, up to the extent of service rendered in
Defence plus 3 years, 5 years for candidates who have ordinarily been domiciled in the state
of Jammu & Kashmir.
Note: For PWD candidates, age relaxation by 10 years for UR persons with disabilities,
13 years for OBC & 15 years for SC/ST PwD candidates.
13 years for OBC & 15 years for SC/ST PwD candidates.
Education Qualification: Applicants should have degree from recognized University
or its equivalent, typing proficiency in English/ Hindi on computer is essential.
or its equivalent, typing proficiency in English/ Hindi on computer is essential.
- Start date for apply online process: 26th December 2015 (Available Now)
- Last date for submission of online application: 25th January 2016
- Last date for take Re-Print of your Application form: 25th January 2016.
- Tentative Exam Date: March – May 2016.
- Start submission of Online Fee: 26th December 2015.
- Last Date for Online Fee Submission: 25th January 2016.
- Start submission of Application Fee at offline: 28th December 2015.
- Last Date for Offline Fee Submission: 22nd January 2016.
Indian Railway going to release recruitment advertisement RRB Advt 03/2015 in which RRBs
will invites applications for filling 18252 vacant seats in different departments. Candidates can
apply for these vacancies to any one RRB only through online RRB Recruitment 2016 application
mode by visiting the website of RRBs concerned in below table. We provided some steps and
links which helps you can apply easily. Candidates are advised to indicate their personal
mobile no. and personal valid e-mail ID in the form.
will invites applications for filling 18252 vacant seats in different departments. Candidates can
apply for these vacancies to any one RRB only through online RRB Recruitment 2016 application
mode by visiting the website of RRBs concerned in below table. We provided some steps and
links which helps you can apply easily. Candidates are advised to indicate their personal
mobile no. and personal valid e-mail ID in the form.
- Click on below Apply online link.
- Fill personal details/ bio data, fee paid etc carefully.
- Pay examination fee through SBI Challan or Computerized post office pay-In slip mode.
- Upload photograph & signature in application form.
- After that submit of application & take print out for future use.
Click here – RRB Exam Syllabus & Exam Pattern <——
- See more at: http://www.result24.co.in/rrb-recruitment.html#sthash.OQDxFp1R.dpuf
Last Updated Wednesday, December 30, 2015
Government of India, Ministry of Railways, Railway Recruitment Boards (RRB) invites
Online Applications from Eligible Indian Citizens for recruitment of following Non Technical
Graduate Popular Categories posts for fill up total 18252 Vacancies of various Zonal
Railways / Production Units on Indian Railways in 2015-16. The closing date for Online
Registration is 25th January 2016.
INDICATIVE CENTRALISED EMPLOYMENT NOTICE NO: 03/2015
Name of the
Post |
Total No of Vacancies
|
Commercial
Apprentice (CA) |
703 (Ahmedabad (WR) - 29, Allahabad (NCR) -
20, Ajmer (NWR) - 16, Bangalore (SWR) - 32, Bhopal (WR) - 01, Bhubaneswar (ECoR) - 09, Bilaspur (SECR) - 05, Bilaspur (CR) - 17, Chennai (SR) - 105, Gorakhpur (NER) - 62, Kolkata (ER) - 82, Malda (SER) - 24, Mumbai (CR) - 129, Secunderabad (SCR) - 85, Secunderabad (ECoR) - 12, Thiruvananthapuram (SR) – 74, Allahabad (NR) (PWD) - 01) |
Traffic Apprentice
(TA) |
1645 (Ahmedabad (WR) - 49, Allahabad (NCR) -
134, Allahabad (NR) - 96, Ajmer (NWR) - 44, Bangalore (SWR) - 121, Bhopal (WCR) - 57, Bhopal (WR) - 06, Bhubaneswar (ECoR) - 58, Bilaspur (CR) - 06, Bilaspur (SECR) - 04, Chandigarh (NR) - 30, Chennai (SR) - 127, Guwahati (NFR) - 74, Gorakhpur (NER) - 52, Jammu Srinagar (NR) - 34, Kolkata (ER) - 95, Mumbai (CR) - 174, Mumbai (WR) - 39, Patna (ECR) - 11, Ranchi (ECR) - 28, Secunderabad (SCR) - 8179, Secunderabad (ECoR) - 44, Siliguri (NFR) - 94, Thiruvananthapuram (SR) – 87, Mumbai (CR) (PWD) - 02) |
Enquiry-cum-
Reservation Clerk (ECRC) |
127 (Ahmedabad (NCR) - 60, Guwahati (NFR) -
17, Jammu Srinagar (NR) - 08, Kolkata (SER) - 23, Siliguri (NFR) - 13, Allahabad (NCR) (PWD) - 02, Allahabad (NR) (PWD) - 04) |
Goods Guard
|
7591 (Ahmedabad (WR) - 392, Allahabad (NCR) -
1350, Allahabad (NR) - 184, Ajmer (NWR) - 199, Ajmer (WCR) - 333, Bangalore (SWR) - 184, Bhopal (WCR) - 585, Bhopal (WR) - 167, Bhubaneswar (ECoR) - 509, Bilaspur (CR) - 44, Bilaspur (SECR) - 05, Chandigarh (NR) - 123, Chennai (SR) - 182, Guwahati (NFR) - 113, Gorakhpur (NER) - 59, Jammu Srinagar (NR) - 52, Kolkata (ER) - 400, Maida (SER) - 97, Mumbai (CR) - 234, Mumbai (WR) - 64, Mumbai (SCR) - 04, Muzaffarpur (ECR) - 335, Patna (ECR) - 579 , Ranchi (ECR) - 389, Secunderabad (SCR) - 357, Secunderabad (ECoR) - 475, Siliguri (NFR) - 72, Thiruvananthapuram (SR) - 96, Allahabad (NCR) (PWD) - 01, Mumbai (CR) (PWD) - 07) |
Junior Accounts
Assistant-cum- Typist (JAA) |
1205 (Ahmedabad (NCR) - 62, Bangalore (SWR)
- 75, Bhopal (WCR) - 100, Bhubaneswar (ECoR) - 59, Bilaspur (SECR) - 118, Chennai (ICF) - 13, Chennai (SR) - 80, Gorakhpur (NER) - 117, Jammu Srinagar (RCF) - 08, Kolkata (SER) - 08, Maida (SER) - 03, Mumbai (CR) - 281, Mumbai (WR) - 150, Ranchi (SER) - 08, Thiruvanthapuram (SR) - 30, Mumbai (CR) (PWD) - 41, Mumbai (WR) (PWD) - 52) |
Senior Clerk-
cum-Typist |
869 (Allahabad (NCR) - 12, Allahabad (NR) - 18,
Ajmer (NWR) - 58, Ajmer (WCR) - 02, Bangalore (SWR) - 33, Bhopal (WCR) - 55, Bhubaneswar (ECoR) - 19, Bilaspur (SECR) - 08, Chandigarh (NR) - 38, Chandigarh (NR Store) - 27, Chennai (SR) - 73, Chennai (ICF) - 03, Guwahati (NFR) - 13, Gorakhpur (NER) - 22, Gorakhpur (RDSO) - 05, Jammu Srinagar (DMW) - 08, Kolkata (ER) - 157, Kolkata (CLW) - 11, Kolkata (SER) - 16, Maida (SER) - 21, Mumbai (CR) - 75, Mumbai (SCR) - 09, Ranchi (SER) - 32, Secunderabad (SCR) - 32, Secunderabad (ECoR) - 32, Siliguri (NFR) - 09, Thiruvananthapuram (SR) - 16, Allahabad (NCR) (PWD) - 06, Allahabad (DLW) (PWD) - 04, Mumbai (CR) (PWD) - 20, Mumbai (WR) (PWD) - 39) |
Assistant Station
Master (ASM) |
5942 (Ahmedabad (WR) - 713, Allahabad (NCR) -
613, Allahabad (NR) - 1268, Ajmer (NWR) - 339, Ajmer (WCR) - 97, Bangalore (SWR) - 165, Bhopal (WCR) - 55, Bhopal (WR) - 125, Bhuba neswar (ECoR) - 116, Bilaspur (SECR) - 10, Bilaspur (CR) - 85, Chandigarh (NR) - 86, Chennai (SR) - 393, Guwahati (NFR) - 192, Jammu Srinagar (NR) - 61, Kolkata (ER) - 450, Maida (SER) - 133, Mumbai (CR) - 763, Mumbai (WR) - 124, Mumbai (SCR) - 89, Muzaffarpur (ECR) - 129, Patna (ECR) - 124, Ranchi (ECR) - 105, Secunderabad (SCR) - 335, Secunderabad (ECoR) - 91, Siliguri (NFR) - 91, Thiruvananthapuram (SR) - 185, Allahabad (NCR) (PWD) - 05) |
Traffic
Assistant |
166 (Kolkata (MR))
|
Senior Time
Keeper |
04 (Allahabad (DLW))
|
Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, Bilaspur, Chandigarh, Chennai, Gorakhpur, Guwahati, Jammu-Srinagar.
Kolkata, Malda, Mumbai, Muzaffarpur, Patna, Ranchi, Secunderabad, Siliguri, Thiruvananthapuram.
Age Limit: 18 to 32 Years as on 1st January 2016. Age Relaxation 05 Years for SC / ST, 03 Years
for OBC, For others as per Rules.
Educational Qualification:
(1) Degree from recognized University or its equivalent.
(2) Typing Proficiency in English / Hindi in Computer is essential for JCAA / Senior Clerk cum
Typist / Senior Time Keeper Posts.
Pay and Grade Pay:
Commercial Apprentice / Traffic Apprentice -> ₹ 9300 - 34800/- + GP ₹ 4200/-
ECRC / Goods Guard / Senior Clerk-cum-Typist / ASM / Senior Time Keeper -> ₹ 5200 - 20200 +
GP ₹ 2800/-
Traffic Assistant -> ₹ 5200 - 20200 + GP ₹ 2000/-
Examination Fee: For UR/OBC male candidates are required to pay examination fee is ₹
100/-. No examination fee for candidates belonging to SC/ST/Ex-Servicemen / Women /
Minorities / Trans-genders / Persons with Disabilities and Economically backward classes.
The fee can be made through SBI/ Post office challan.
Selection Process: Common single stage CBT (Computer Based Test) / Examination to
be held simultaneously by all participating RRBs [Same Day(s)] tentatively during MARCH -
MAY, 2016.
How to Apply: Eligible Interested Candidates are required to fill Online Application through
any one Participating RRB Official Website from 26/12/2015 and Registration end on
25/01/2016 up to 23:59 Hours.

Important Dates:
Online Registration start from -> 26/12/2015
Date & Time of Closing of online Registration -> 25/01/2016 up to 23.59 Hrs
Last Date for Reprint of Application -> 25/01/2016 up to 23.59 Hrs
Tentative Dates / Slot of Common Computer Based Test / Examination -> March - May, 2016
Online Fee payment -> 26/12/2015 to 25/01/2016
Offline Fee payment (through SBI / Post office challan) -> 28/12/2015 to 22/01/2016
| Detailed Employment Notification >> | RRB ONLINE REGISTRATION >> |
| Apply Online (RRB Chennai) >> | Railway Recruitment 2016 Jobs List >> |
Read more: RRB Recruitment 2016 Apply Online (18252 Vacancies Non Technical Graduate)
http://www.indgovtjobs.in/2015/12/RRB-Recruitment-Centralised.html#ixzz3xVSdPQyZ
सोमवार, 4 जनवरी 2016
Earn from Your Home, Earning website for Students, Job-less people
http://Earn4InviteFriends.com/?ref=19091
http://RewardnCash.com/?ref=19091
Only one Click.....
You can Earn 500 Dollars Today, Check Tasks after creating account and login to
your account pa
एक ऐसी वेबसाइट जहा सिर्फ आपको वेबसाइट को ओपन करना है और उस वेबसाइट पे आपको अपनी आईडी बनानी है जिसमे सिर्फ 1मिनट टाइम लगेंगे।
होते ही आपको 20 डॉलर मिल जायेंगे।
और वहा आपको आपके आईडी की रेफेर लिंक मिलंगे उस लिंक को आपको फेसबुक पेव्हाट्सएप्प पे और भी सोशल मीडिया साईट पे शेयर करना है, आपके लिंक पे पर क्लिक 5डॉलर मिलेंगे।
ये फेक नही है दोस्तों आप कम से कम एक बार वेबसाइट ओपन कर के देख लीजिये अगर आपको फेक लगे तो regester नही करना।
सोचिये अगर आपके लिंक के अगर 20 लोग भी क्लिक करते हैं तो आपको 100डॉलर मिलेंगे मतलब की 6600रूपये।
विजिट लिंक:
Try करने में क्या हर्ज है दोस्तों वैसे भी आपको यहा कोई एप्प नही डाऊनलोड करना है।
नोट:- आप जितने भी इनकम करोगे उस पैसे को अपने बैंक अकाउंट में ट्रान्सफर कर सकते है
Only one Click and so on....
http://Earn4InviteFriends.com/?ref=19091
http://RewardnCash.com/?ref=19091
Only one Click.....
 | Everyone can join the site Unlimited Job Positions! Anyone can Join! No Experience required! Instant Account Setup and Money Making! No joining fee |  |
your account pa
| |||||
होते ही आपको 20 डॉलर मिल जायेंगे।
और वहा आपको आपके आईडी की रेफेर लिंक मिलंगे उस लिंक को आपको फेसबुक पेव्हाट्सएप्प पे और भी सोशल मीडिया साईट पे शेयर करना है, आपके लिंक पे पर क्लिक 5डॉलर मिलेंगे।
ये फेक नही है दोस्तों आप कम से कम एक बार वेबसाइट ओपन कर के देख लीजिये अगर आपको फेक लगे तो regester नही करना।
सोचिये अगर आपके लिंक के अगर 20 लोग भी क्लिक करते हैं तो आपको 100डॉलर मिलेंगे मतलब की 6600रूपये।
विजिट लिंक:
Try करने में क्या हर्ज है दोस्तों वैसे भी आपको यहा कोई एप्प नही डाऊनलोड करना है।
नोट:- आप जितने भी इनकम करोगे उस पैसे को अपने बैंक अकाउंट में ट्रान्सफर कर सकते है
Only one Click and so on....
http://Earn4InviteFriends.com/?ref=19091
सदस्यता लें
टिप्पणियाँ (Atom)


